Table of Contents
ToggleRepo Rate Decoded: Why RBI Changes It & What It Means?
Why Repo Rate Matters to Every Indian?
Repo rate affects every Indian, whether you take loans or not. Whenever the RBI changes the repo rate, it directly impacts borrowing costs, EMIs, inflation, and overall economic growth.
For example, when the repo rate is reduced, banks can borrow money from the RBI at a lower cost. This helps them offer loans at cheaper rates to the public – resulting in lower EMIs and easier access to credit.
On the other hand, when inflation rises and everything becomes expensive, the RBI repo rate is increased to make borrowing costlier. Higher interest rates slow down loans and reduce excess spending, helping control inflation.
Economic growth is also closely linked to repo rate decisions. When loans become affordable, businesses invest more, people spend more, and the economy gets a positive push. When loans become expensive, growth naturally slows down.
What Is Repo Rate? Simple Meaning Explained
The repo rate is the interest rate at which the central bank (RBI) lends money to commercial banks when they face a shortage of funds. These short-term loans are given against government securities, usually treasury bills or government bonds.
In simple words, repo rate meaning refers to the repurchase rate–because banks sell their securities to the RBI with an agreement to buy them back later at a fixed price.
This monetary policy tool helps the RBI control inflation, manage liquidity in the banking system, and ensure stability in the economy.
How Repurchase Rate Works (With a Simple Scenario)?
The RBI rate explains the borrowing relationship between the RBI and commercial banks. Whenever a bank needs short-term funds, it can approach the RBI and borrow money by giving government securities as collateral.
For example, imagine HDFC Bank needs additional funds. It can borrow from the RBI by submitting government bonds worth ₹100 crore. The interest rate that RBI charges on this borrowing is the repo rate.
When the this rate is low, banks can borrow money at cheaper rates, which allows them to offer home loans, business loans, and personal loans to customers at lower interest rates. But when the repo rate increases, borrowing becomes expensive for banks, and EMIs for common people also rise.
How does it control liquidity?
In simple words, liquidity means how easily money flows in the economy.
- If the RBI wants to reduce liquidity, it increases the repo rate. Banks borrow less because it becomes costlier, so money supply in the system slows down.
- If the RBI wants to increase liquidity, it reduces the repo rate. Banks borrow more at cheaper rates, and this increases the flow of money in the economy.
This is how the RBI manages loan affordability, inflation, and
RBI Repo Rate: Why RBI Changes It Over Time?
The RBI repo rate is not fixed. It keeps changing based on the country’s economic situation. The repo rate by RBI is adjusted to manage inflation, control money supply, and support economic growth. These decisions are taken by a group called the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)–a team responsible for reviewing India’s financial conditions every two months and deciding whether the repo rate should be increased, decreased, or kept unchanged.
Why RBI Increases the Lending Rate?
RBI increases the repo rate mainly when the economy is overheating or inflation is rising. A higher repo rate makes borrowing expensive for banks, which later reduces loans to the public. This helps slow down the flow of money and control excess spending.
RBI usually increases the repo rate to:
- Control high inflation
- Reduce unnecessary spending
- Balance demand and supply
- Prevent the economy from overheating
In simple words, when prices of everyday goods keep rising, increasing the repo rate helps cool down the economy.
Why RBI Decreases the Lending Rate?
RBI reduces the repo rate when the economy needs support. A lower repo rate makes borrowing cheaper for banks, which helps them offer low-interest loans to people, small businesses, and large companies. This increases economic activity and gives the system a much-needed push.
RBI decreases the repo rate to:
- Increase money flow in the market
- Support businesses during tough times
- Boost spending and investments
- Help control economic slowdown
For example, imagine the country is facing a recession–jobs are declining, stock markets are falling, and businesses are struggling. In such situations, reducing the repo rate helps revive the economy. Lower interest rates encourage businesses to take loans, restart operations, hire employees, and build stability. Even common people benefit through lower EMIs and better credit access.
During an economic slowdown, markets often turn volatile. If you want to stay prepared, don’t miss my Stock Market Crash Survival Guide
Role of the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)
The MPC is a small committee within the RBI that meets every two months. They study inflation, growth, global conditions, banking data, and market behavior. Based on all this, they decide whether the repo rate should:
- go up,
- go down, or
- stay the same.
Their decisions directly shape how the economy moves.
overall economic stability using the repo rate.
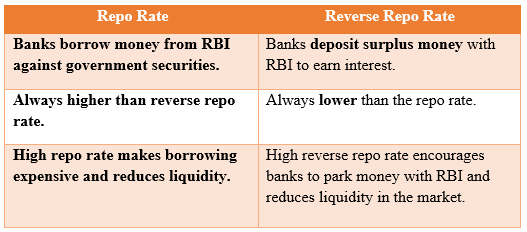
Reverse Repo Rate Explained: Meaning & Key Difference
The reverse repo rate is the interest rate at which commercial banks deposit their surplus funds with the RBI and earn interest on it. In simple words, when banks have extra money, they can “park” it with the RBI instead of lending it to the public.
For example, just like you and I deposit our extra savings in a bank to earn interest, commercial banks do the same with the RBI. They deposit their unused funds with the central bank and earn interest based on the reverse repo rate.
Reverse repo rate also affects the economy.
- When the reverse repo rate increases, banks prefer to deposit more money with the RBI rather than lending it to people or businesses. This reduces the money flow in the economy and helps control inflation.
- When the reverse repo rate decreases, banks are encouraged to lend more instead of depositing with the RBI, which increases liquidity and supports economic activity.
Quick Comparison: Repo Rate vs Reverse Repo Rate
Why Both Rates Matter?
Both the rate are essential tools for balancing the economy.
- Repo rate controls how much banks can borrow, influencing loan interest rates and EMIs.
- Reverse repo rate controls how much banks are willing to lend, influencing liquidity and money supply.
Together, they help RBI maintain financial stability, control inflation, and guide the flow of money in the economy.
FAQs: Quick and Simple Answers
1. Why does RBI change the repurchase rate?
RBI changes the repo rate to control inflation, manage money supply, and support economic growth. Raising the rate reduces borrowing and slows spending, while lowering it makes loans cheaper and boosts economic activity.
2. What is the difference between repo rate and reverse repo rate?
The repo rate is what banks pay when they borrow from RBI, while the reverse repo rate is what banks earn when they deposit surplus funds with RBI. Repo gives liquidity; reverse repo absorbs liquidity.
3. How often does RBI review the repurchase rate?
RBI reviews the repurchase rate every two months during the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting. However, in unusual economic situations, RBI can change the rate outside the scheduled review.
4. Is repo rate the same as home loan interest rate?
No. The repo rate influences home loan rates but is not the rate you pay. Banks add their own margin (spread) over the repo-linked lending rate to decide your final home loan interest.
5. How does a change in repurchase rate affect home loan EMIs?
When the repo rate increases, banks borrow at a higher cost and raise loan interest rates, causing EMIs to rise. When the central bank rate falls, borrowing becomes cheaper, and EMIs generally decrease.
Conclusion: The Repo Rate Shapes India’s Financial Pulse
This rate may sound technical, but it quietly shapes our daily financial decisions. From EMIs to inflation, from business growth to the overall money flow in the economy–everything moves in response to RBI’s rate changes. Understanding how the repo rate works helps you make smarter choices with your money, no matter what the market looks like.
As long as money exists, the lending rate will remain one of the most important signals in India’s financial system.
If you want to protect your savings during rising prices, don’t miss my guide on 7 Proven Ways to Protect Money from Inflation.
Thanks for reading – stay informed, stay financially confident.
Book Recommendations to Master an Inflation-Proof Mindset
If you truly want to protect and grow your money, then it’s not just about strategies — it’s about sharpening your mindset. These books have helped thousands of people (including me) rethink how money really works. So if you’re serious about long-term financial growth, add these to your shelf: